Overview Diabetes – Causes, Diagnosis, Symptoms
Diabetes mellitus is a condition that consist of a group of diseases that affect how your body uses blood sugar. Glucose is the primary source of energy for the cells of your muscles and tissues and hence, it is extremely essential for your overall good health. Also, glucose is the main source that is responsible to fuel your brain.
Causes of diabetes
The causes of diabetes vary from the types of diabetes. Each type of diabetes is caused because of a different reason.
- Causes of type 1 diabetes
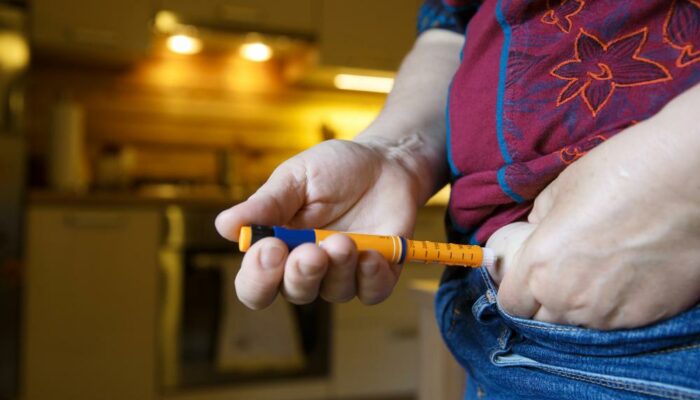
The exact reason that causes type 1 diabetes is unknown. The known fact is that in type 1 diabetes, your immune system which fights harmful bacteria or viruses tends to attack and destroy the insulin-producing cells in your pancreas. This leaves your body with little or no insulin. Hence, sugar builds up in your bloodstream instead of being transferred to your cells where energy is needed. Type 1 diabetes is possibly caused due to the genetic factors and environmental factors. However, the exact cause of type 1 diabetes is unknown. - Causes of gestational diabetes
To sustain a pregnancy, the placenta produces hormones when a woman is pregnant. Your cells become more resistant to insulin because of these hormones. Normally, to overcome this resistance, extra insulin is produced by your pancreas. However, sometimes your pancreas is not able to produce sufficient amount of insulin. As a result, too much of glucose tends to stay in your blood whereas very little gets transferred into your cells. This condition results in gestational diabetes. - Causes of type 2 diabetes and prediabetes
Prediabetes condition can further lead to type 2 diabetes. In both these conditions, your cells tend to develop a resistance to the action of insulin. Also, your pancreas is not able to produce enough of insulin to overcome this resistance. This leads to the building up of glucose in your bloodstream rather than getting transferred in your cells where it is needed. The exact cause of type 2 diabetes is unknown, however, environmental factors and genetic do influence the occurrence. Also, obesity is largely linked to type 2 diabetes however, not everyone who is diagnosed with type 2 diabetes is obese.
Diagnosis of diabetes
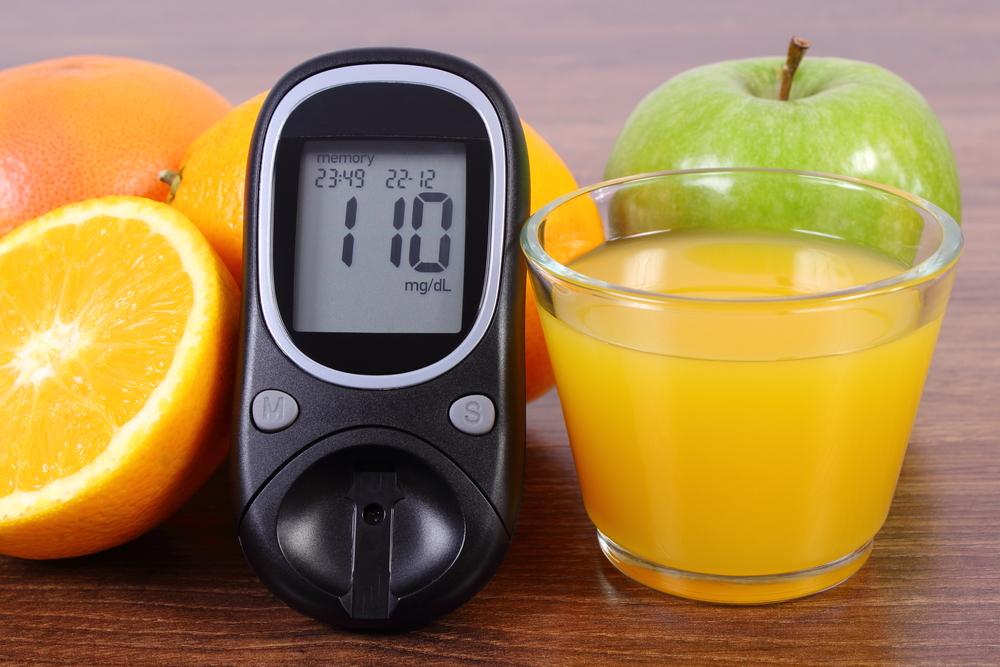
The American Diabetes Association recommends anyone with a body mass index higher than 25 or anyone who is older than 45 to get screened for diabetes. Glycated hemoglobin (A1C) test, oral glucose tolerance test, random blood sugar test, and fasting blood sugar test are the tests to diagnose prediabetes, type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Symptoms of diabetes
Depending on how much your blood sugar is elevated, the symptoms of diabetes may vary from person to person. Those who are diagnosed with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes may not experience any visible symptoms initially. Also, in type 1 diabetes, the symptoms tend to appear quickly and tend to become more severe. Symptoms of type 1 and type 2 diabetes are-
- Frequent urination
- Unexplained weight loss
- Presence of ketones in your urine
- Extreme hunger
- Increased thirst
- Irritability
- Slow-healing sores
- Blurred vision
- Fatigue
- Irritability
- Frequent infections
If you observe any of the above symptoms, you must consult your doctor immediately. The sooner the condition is diagnosed, the sooner it can be controlled.